Diabetes is possibly the most misunderstood medical condition humanity has ever had to deal with. It’s a silent but rapidly growing pandemic that is sweeping across the globe and significantly impacting millions of lives. According to a World Health Organization fact sheet, the global prevalence of diabetes among adults has risen from 108 million cases in 1980 to more than 422 million in 2019. This surge is mainly due to changes in lifestyle, including unhealthy diets rich in processed and sugary foods, sedentary behavior, and a lack of regular physical activity.
The rise in diabetes is not just a concern for those diagnosed; it also presents a significant challenge for their family members and caregivers. As the incidence of diabetes increases, so does the likelihood that we may find ourselves in a caregiving role for a loved one battling this chronic condition. This role, often unexpected, requires a deep understanding of the disease, its management, and the physical and emotional support needed by those affected. With this guide, we hope to empower caregivers to transform the challenge of diabetes care into an opportunity for nurturing, growth, and resilience.
Understanding Diabetes and Its Impact
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects the body's ability to regulate blood sugar levels. There are two types of diabetes. Type 1 Diabetes is an autoimmune disease that causes the pancreas to stop functioning so the body doesn't produce insulin. In the case of Type 2 diabetes, the body produces insulin but cannot use it effectively. Another key difference is that Type 1 usually manifests at a young age and is not genetic or related to lifestyle. Type 2 Diabetes, on the other hand, usually develops much later in life and is frequently attributed to poor lifestyle choices.
Understanding the type of diabetes your loved one has is crucial as it influences the care approach. For instance, Type 1 diabetes almost always requires insulin injections, while Type 2 diabetes can sometimes be managed with lifestyle changes and oral medications. It’s also important to understand that diabetes cannot be cured. With Type 2, lifestyle and diet changes can reverse the effects to the extent that a patient can get along without medication, but this requires a life-long commitment.
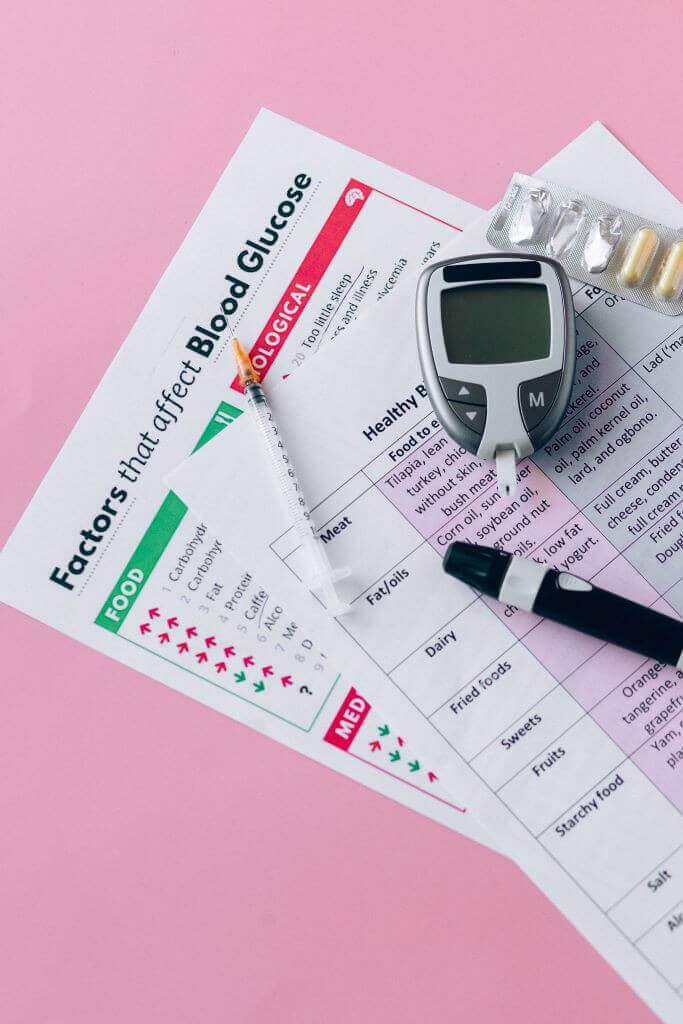
Diabetes can lead to serious health complications if not managed properly, including heart disease, kidney damage, vision loss, and nerve damage. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels, adherence to medication, and lifestyle modifications are key to managing these risks. As a caregiver, understanding these potential complications can help you recognize early signs and seek timely medical intervention.
Daily Diabetes Management
Regular blood sugar monitoring is the cornerstone of diabetes management. It helps to understand how food, physical activity, and medication affect blood sugar levels. As a caregiver, you can assist in maintaining a log of readings to share with healthcare providers for better treatment planning. This log can also help identify patterns and triggers that cause blood sugar fluctuations.
The other critical element is proper medication management to maintain blood sugar levels within healthy limits. This includes ensuring medications are taken as prescribed, understanding their side effects, and knowing how to handle missed doses. As a caregiver, you can help by setting reminders and overseeing medication administration, ensuring the prescribed regimen is followed accurately.
Nutrition and Diabetes
A balanced diet can play a significant role in managing diabetes. Understanding how different foods affect blood sugar levels makes meal planning easier and reduces the patient’s dependence on insulin or medications. There are several factors that determine whether or not foods are diabetic-friendly. The most important are carbohydrates and fiber, as they directly impact blood sugar levels. Other factors, such as fat or protein content, should also be considered as they influence overall health and, in turn, could indirectly influence blood sugar.
Changing ingrained dietary habits isn’t easy; it takes time and determination. However, getting nutrition right is one of the best ways to manage blood sugar, so, as a caregiver, it pays to understand this. At first, fine-tuning a nutrition plan may seem daunting and be a bit hit-and-miss. It helps to have some nutritional supplements on hand to ensure you can strike the best balance between carbs and calories. For the best range of products and expert advice, contact the team at LL Medico. We have more than 25 years of experience in elder care products. You can call us at (855) 422-4556 or email us at support@llmedico.com.
Physical Activity and Diabetes
Regular exercise burns calories and helps to manage blood sugar levels. It also reduces the risk of heart disease and improves overall health. As a caregiver, you can encourage and facilitate daily physical activities that are enjoyable and suitable for the individual's health condition. This could range from simple exercises like walking or gardening to more structured activities like yoga or swimming. For more information on this, you can read this blog.
While exercise is beneficial, safety precautions are necessary to prevent low blood sugar levels or hypoglycemia. This is a condition that can be fatal if not rectified quickly. You should ensure that a source of quick-acting sugar is available at all times. Although diabetic patients can usually feel when their blood sugar is low, it may be prudent to check the level after exercise just to be sure.
Emotional Support and Coping
Living with diabetes is challenging. Stress, depression and anxiety are common and can affect diabetes management. As a caregiver, you can and should provide emotional support, encourage open communication about feelings and seek professional help when necessary. If you’re new to this, it will be very scary at first. You’re not the first person to face this challenge, and you’re not alone. Get in touch with caregiver associations like the National Alliance for Caregiving or the Family Caregiver Alliance to get guidance on every aspect of caregiving.
Caring for anyone is difficult, but diabetes adds a few extra challenges. Don’t be under any illusion; this role will take its toll on you. In order to cope with the mental and physical burden of caring for someone with a chronic, life-threatening condition, you need to pay much closer attention to your own health and wellbeing. You can find a lot of helpful information and tips in this blog.
In closing
Caring for someone with diabetes can be challenging, but remember, your support and care can make a significant difference in their life. It's about understanding their needs and providing physical and emotional support. As you navigate this journey, remember the words of Albert Schweitzer, "Constant kindness can accomplish much. As the sun makes ice melt, kindness causes misunderstanding, mistrust, and hostility to evaporate." Your kindness, patience, and dedication can help your loved one live a fulfilling life with diabetes.






 855-422-4556
855-422-4556 Chat
Chat E-Mail
E-Mail Monday - Friday 9:00AM to 5:00PM EST
Monday - Friday 9:00AM to 5:00PM EST




 Shopping With LL Medico
Shopping With LL Medico



 855-422-4556
855-422-4556